

Use an LLM to translate a function’s help documentation on
the fly. lang overrides the ? and
help() functions in your R session. If you are using
RStudio or Positron, the translated help page will appear in the ‘Help’
pane.
To install the GitHub version of lang, use:
install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("mlverse/lang")langIn order to work, lang needs two things:
An LLM connection
A target language (e.g.: Spanish, French, Korean)
These two can be defined using lang_use(). For example,
the following code shows how to use OpenAI’s GPT-4o model to translate
lm()’s help into Spanish:
library(lang)
chat <- ellmer::chat_openai(model = "gpt-4o")
lang_use(backend = chat, .lang = "spanish")
?lm
#> [1/7] ■■ 4% | Title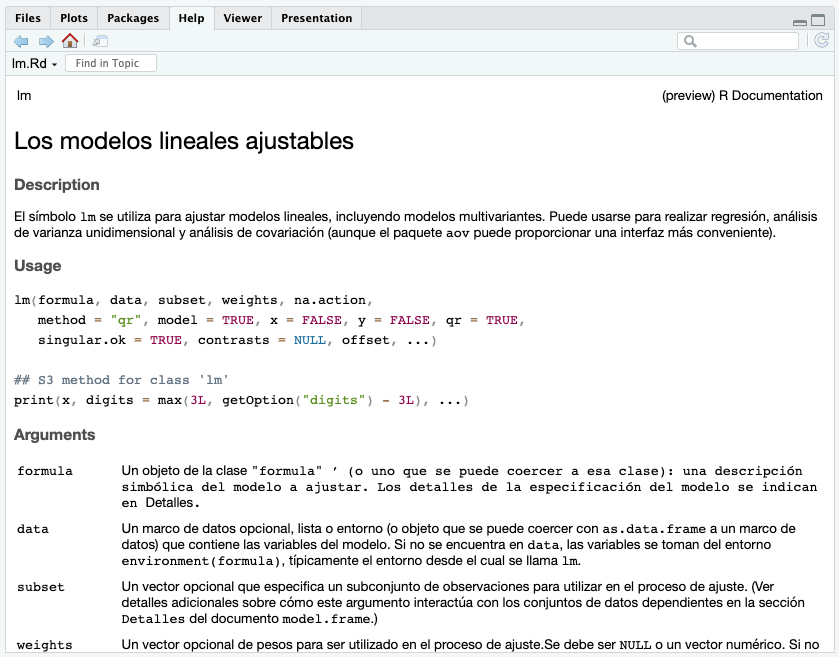
After setup, simply use ? to trigger and display the
translated documentation. During translation, lang will
display its progress by showing which section of the documentation is
currently translating. During the R session, if you request the same R
function’s help more than one time then lang will use its
cached results, which will run immediately.
R enforces the printed names of each section, so they cannot be translated. This means that titles such as “Description”, “Usage” and “Arguments” will always remain untranslated.
There are two ways to define the LLM in lang_use():
Use an ellmer chat
object:
lang_use(backend = ellmer::chat_openai(model = "gpt-4o"))Use local LLMs available through Ollama. Pass "ollama" as the
backend argument, and specify which installed model to
use:
lang_use(backend = "ollama", model = "llama3.2", seed = 100)Under the hood, lang uses the ollamar
package to integrate with Ollama. Any additional arguments, such as
seed as shown above, will be passed as-is to
ollamar’s chat() function.
In order of priority, these are the ways in which lang
determines the language it will translate to:
.lang when calling
lang_use()LANGUAGE environment variableLANG environment variableIt is likely that your LANG variable already defaults to
your locale. For example, mine is set to: en_US.UTF-8 (That
means English, United States). For someone in France, the locale would
be something such as fr_FR.UTF-8. Llama3.2, recognizes
these UTF locales, and using lang, calling ?
will result in translating the function’s help documentation into
French.
If both environment variables are set, and are different from each
other, lang will display a one-time message indicating
which value it will use. If the target language is English,
lang will re-route help calls back to base R.
To check the current target language at any point during the R
session, simply run: lang_use(), with no arguments, and it
will print out the current settings, which include language:
lang_use()
#> Model: gpt-4o via OpenAI
#> Lang: spanishBy default, lang will cache the translations it performs
in a temporary folder. If R is restarted, a new folder will be used.
If you notice that you are translating the same function’s help over
and over and across different R sessions, then fixing the cache location
would be helpful. Use .cache to define the folder:
lang::lang_use(
backend = "ollama",
model = "llama3.2",
.cache = "~/help-translations/",
.lang = "spanish"
)If lang becomes a regular part of your workflow, and
running lang_use() at the beginning of every R session
becomes cumbersome, then consider letting R connect at start up.
If present, the .Rprofile file runs at the beginning of any
R session. If you wish to automatically set the model and language to
use, add a call to llm_use() to this file. You can call
usethis::edit_r_profile() to open your .Rprofile file so
you can add the option.
Here is an example of such a call that could be used in the .Rprofile file:
lang::lang_use(
backend = "ollama",
model = "llama3.2",
.cache = "~/help-translations/",
.lang = "spanish",
.silent = TRUE
)In the example, we set .silent to TRUE so
that there is no message every time the R session is restarted.
As you can imagine, the quality of translation will mostly depend on the LLM being used. This solution is meant to be as helpful as possible, but we acknowledge that at this stage of LLMs, only a human curated translation will be the best solution. Having said that, I believe that even an imperfect translation could go a long way with someone who is struggling to understand how to use a specific function in a package and may also struggle with the English language.
If the original English help page displays, check your environment variables:
Sys.getenv("LANG")
#> [1] "en_US.UTF-8"
Sys.getenv("LANGUAGE")
#> [1] ""In my case, lang recognizes that the environment is set
to English, because of the en code in the variable. If your
LANG variable is set to en_... then no
translation will occur.
If this is your case, set the LANGUAGE variable to your
preference. You can use the full language name, such as ‘spanish’, or
‘french’, etc. You can use
Sys.setenv(LANGUAGE = "[my language]"), or, for a more
permanent solution, add the entry to your your .Renviron file
(usethis::edit_r_environ()).
malllang uses the mall package to produce the
translations. To avoid conflicts in the setup and use of both packages
during the R session, lang runs mall in a
separate R process which is only alive while translating the
documentation. This means that you can have a specific LLM setup for
lang, and a different one for mall during your
R session.